Code for helper functions.
More...
◆ AngleToVector()
| const Vector2 AngleToVector |
( |
const float |
theta | ) |
|
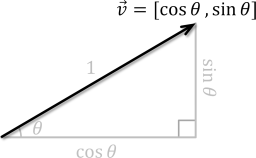
Compute a unit vector at an angle measured in radians counterclockwise from the positive X-axis. If \(\vec{v} = [v_x, v_y]\) is a unit vector with tail at the Origin and \(\theta\) is the angle between \(\vec{v}\) and the positive X-axis, then \(\sin \theta = v_y\) and \(\cos \theta = v_x\). Hence, \(\vec{v} = [\cos \theta, \sin \theta]\), as shown below. Therefore, this function returns Vector2(cosf(theta), sinf(theta)).
- Parameters
-
- Returns
- Unit vector at angle theta counterclockwise from positive X.
◆ GetCollisionInfo() [1/2]
| bool GetCollisionInfo |
( |
const float |
a, |
|
|
const float |
b, |
|
|
const float |
r, |
|
|
float & |
d |
|
) |
| |
Get collision information for a circle intersecting a line segment given that neither end point of the line is inside the circle. The result will not be valid if either end point is inside the circle. All computation is done in one dimension only, and therefore can be used for both the x-axis and the y-axis if desired.
- Parameters
-
| a | One end of the line segment. |
| b | The other end of the line segment. |
| r | Radius of the circle. |
| d | [out] Overlap distance. |
- Returns
- true if the circle overlaps the line.
◆ GetCollisionInfo() [2/2]
| bool GetCollisionInfo |
( |
BoundingBox |
b, |
|
|
BoundingSphere |
s, |
|
|
Vector2 & |
norm, |
|
|
float & |
d |
|
) |
| |
Get collision information for a circle intersecting an AABB.
- Parameters
-
| b | An AABB. |
| s | A bounding sphere. |
| norm | [out] The collision normal. |
| d | [out] The overlap distance. |
- Returns
- true if the AABB overlaps the bounding sphere.
◆ NormalizeAngle()
| void NormalizeAngle |
( |
float & |
theta | ) |
|
Normalize an angle in radians to \(\pm\pi\). If the angle is very large or very small, then this function will be very slow. However, it will be very fast if the angle is not too far out of range.
- Parameters
-
| theta | [in, out] An angle in radians. |
◆ VectorNormalCC()
| const Vector2 VectorNormalCC |
( |
const Vector2 & |
v | ) |
|
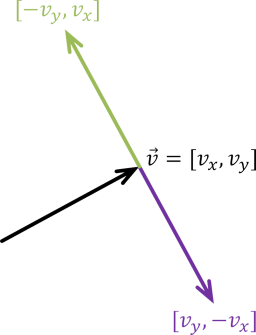
Compute the counterclockwise unit perpendicular to a vector. If \(\vec{v} = [v_x, v_y]\), then both dot products \(\vec{v} \cdot [-v_y, v_x]\) and \(\vec{v} \cdot [v_y, -v_x]\) are equal to zero, and therefore both \([-v_y, v_x]\) and \([v_y, -v_x]\) are perpendicular to \(\vec{v}\). The former (drawn in green below) points counterclockwise from \(\vec{v}\) and the latter (drawn in purple below) points clockwise from \(\vec{v}\). Therefore, this function computes Vector2(-v.y, v.x) and normalizes it before returning it.
- Parameters
-
| v | A vector, not necessarily normalized. |
- Returns
- The counterclockwise unit perpendicular to v.


 1.8.14
1.8.14